Why is the United States obsessed with a 'tariff war'?
On the 2nd local time, US President Trump signed an executive order on the so-called "equivalent tariffs", announcing that the United States would impose a "minimum benchmark tariff" of 10% on trading partners and impose higher tariffs on certain trading partners. The 10% tariff imposed on all trading partners will take effect on the 5th.
The United States has previously announced a 25% tariff on all imported cars and steel and aluminum, and threatened to impose a 200% tariff on EU alcoholic products. Since the Trump administration took office, the United States has frequently raised the "big stick" of tariffs and launched "indiscriminate attacks" on almost all major trading partners, which has caused strong dissatisfaction worldwide and domestically, and has also been countered by many countries.

1、Why did President Trump increase tariffs?
Why does Trump insist on wielding the tariff stick, which goes against his long-standing free trade policy, when he waves the stick and the global capital market is not spared, even Japan has shouted "tariffs shake the foundation of the country", and even the US market has suffered as a result? We believe that historically, the 'tariff war' has become a political tool of the United States rather than an economic measure. Since its founding in 1776, the United States has attempted multiple times to overcome economic difficulties by raising tariffs, but has not achieved the expected results, and even backfired. For example, President Reagan hoped to protect domestic businesses by raising taxes. In reality, tariffs were once the main source of revenue for the US government. White House statistics show that between 1798 and 1913, tariffs accounted for over half of the annual federal government revenue in the United States, reaching as high as 90%. Therefore, the tariff income this time is the only reliable option to relieve the pressure of the upcoming treasury bond, but in the past 70 years, the proportion is only about 2%. This means that the US government is no longer able to make a big profit by raising tariffs, and history has repeatedly proven that high tariffs harm others and do not benefit oneself, leading to international tensions. In fact, after the tariff war began, the United States has also entered a dilemma.
2、Why does President Trump like this policy so much?
Based on the current situation, since tariff weapons cannot cure diseases and may even be fatal, why does the Trump administration still use them? When we look back at American history, we can find that the US tariff policy is deeply influenced by presidential elections, and there is often a political intention behind it to attract votes and consolidate the vote base. McKinley and Hoover both promised during their presidential campaigns to protect their domestic industries and cope with economic downturns by imposing tariffs upon taking office. During Nixon's tenure, political factors were an important basis for his economic decisions; George W. Bush's steel and aluminum tariff policy was also aimed at building popularity for the midterm elections that year.
During his presidential campaign, President Trump repeatedly declared that imposing tariffs would have many benefits. Douglas Owen, an economics professor at Dartmouth College in the United States, pointed out that high tariff commitments have successfully shaped Trump's image as a "protector of American workers" and helped him win votes in key regions, especially the Rust Belt in the Midwest. After returning to the White House, Trump's "tariff obsession" further escalated, seeing it as the "master key" to solving all problems. This is closely related to the current unfavorable voting political atmosphere in the United States.
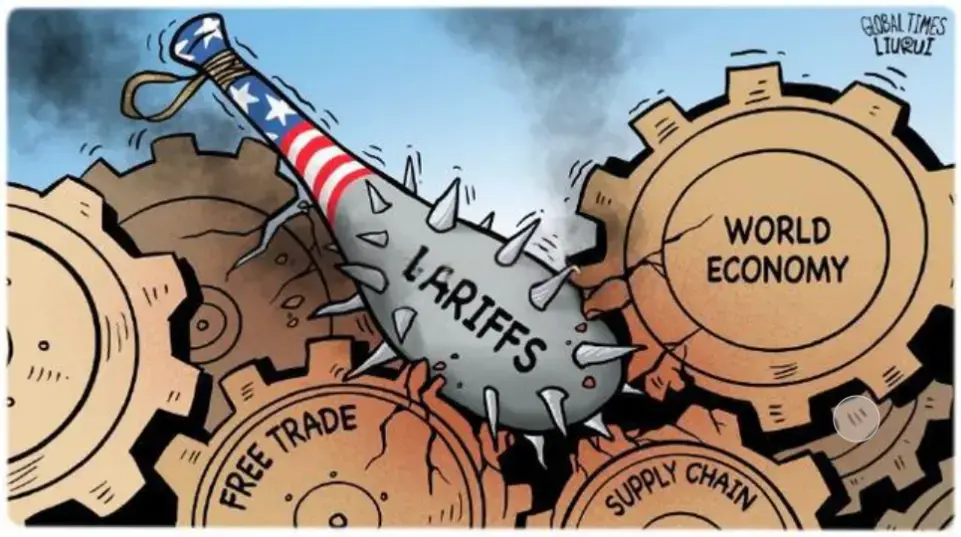

3、What impact will the tariff war have on various countries?
The impact of the tariff war on the United States is mainly reflected in multiple aspects such as economy, politics, and society.
1: In terms of economy, the tariff war has caused multiple blows to the US economy. The United States has imposed high tariffs on many parts of the world, especially on China. The tariffs have gradually increased from the initial 20% to 245%, which has not only caused the United States to lose its huge market in China, but also led to the rupture of the global supply chain. US agricultural exporters, especially soybean exporters, have suffered heavy losses. After China cancelled its trade with the United States, a large number of agricultural products cannot be exported
In addition, the tariff war has increased the probability of the US economy falling into recession, damaged financial market confidence, and led to losses in stocks, bonds, foreign exchange, and credit
2: In terms of politics, the impact of tariff policies will begin to manifest across the United States by the end of next month, especially with a greater impact on low-income populations. Due to the fact that low-income individuals allocate more of their income towards purchasing goods, the increase in tariffs has a more significant impact on them
In addition, the tariff war has also triggered countermeasures from multiple countries around the world, exacerbating international trade tensions
3: In terms of society, the tariff war has led to an increase in unemployment and social instability. The Smoot Hawley Tariff Act in history is an example, which led to a surge in US unemployment, economic deterioration, and ultimately triggered the Great Depression
Although modern society has stronger coping abilities, the connections between all parties are also very close. If the US mishandles the tariff war, not only will similar problems arise, but it will also lead to the reshaping of the international financial order.