Mechanism of Action: Prilocaine's Unique Approach
Prilocaine's mechanism of action sets it apart from other local anesthetics, contributing to its enhanced efficacy. As an amide-type local anesthetic, prilocaine works by blocking sodium channels in nerve cell membranes, effectively preventing the propagation of action potentials. This process inhibits the transmission of pain signals, resulting in localized anesthesia.
Molecular Structure and Lipid Solubility
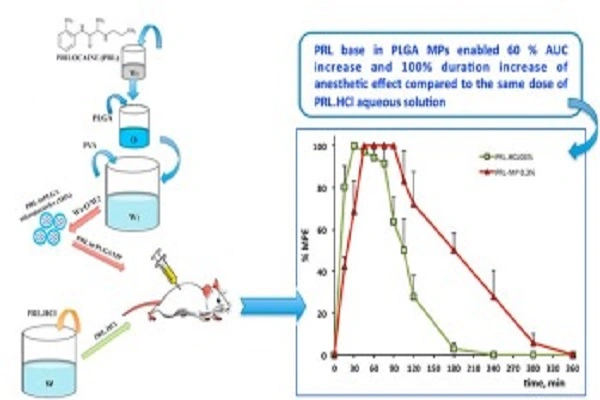
The molecular structure of prilocaine plays a crucial role in its effectiveness. Its balanced lipid solubility allows it to penetrate tissue barriers efficiently, reaching the target nerve fibers quickly. This property contributes to prilocaine's rapid onset of action, typically within 1-2 minutes when used for infiltration anesthesia. High-quality Prilocaine Powder ensures consistent performance, making it a reliable choice for pharmaceutical formulations in local anesthesia applications.
pKa and Tissue Penetration
Prilocaine's pKa esteem, which is somewhat lower than that of numerous other neighborhood anesthetics, improves its capacity to enter tissues viably. This characteristic permits for a more broad spread of the anesthetic impact, especially advantageous in methods requiring a bigger region of anesthesia.
Vasodilatory Effects
Unlike some other local anesthetics, prilocaine exhibits minimal vasodilatory effects. This property can be advantageous in certain clinical situations, as it reduces the risk of systemic absorption and prolongs the duration of local anesthetic action without the need for additional vasoconstrictors.
Comparing Prilocaine to Other Local Anesthetics
When comparing prilocaine powder to other local anesthetics, several factors contribute to its enhanced efficacy and unique position in the field of local anesthesia.
Onset and Duration of Action
Prilocaine typically demonstrates a rapid onset of action, similar to lidocaine. However, its duration of effect is often longer than lidocaine but shorter than bupivacaine. This balanced profile makes prilocaine suitable for a wide range of procedures, from short dental interventions to more extended surgical operations.
Toxicity Profile
One of prilocaine's notable advantages is its lower systemic toxicity compared to many other local anesthetics. This reduced toxicity allows for the use of higher doses when necessary, enhancing its overall efficacy and safety profile. The lower risk of systemic side effects makes prilocaine an attractive option for patients with certain medical conditions or sensitivities.
Tissue Irritation and Allergic Reactions
Prilocaine is known for causing minimal tissue irritation, which can contribute to improved patient comfort during and after procedures. Additionally, the incidence of allergic reactions to prilocaine is relatively low compared to some other local anesthetics, further enhancing its safety profile and clinical utility.
Versatility in Formulations
The powder form of prilocaine offers significant advantages in terms of formulation versatility. It can be easily incorporated into various delivery systems, including creams, gels, and injectable solutions. This flexibility allows for precise dosing and tailored applications across different medical and dental procedures.
Combination Potential
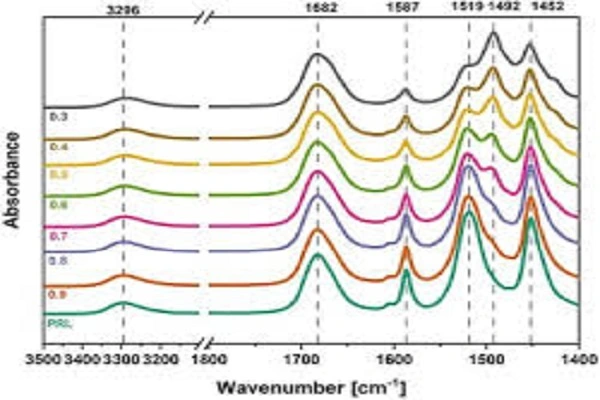
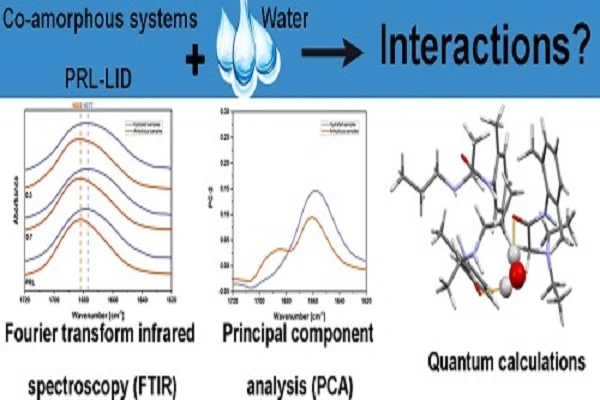
Prilocaine's compatibility with other local anesthetics and additives enhances its efficacy in certain applications. For example, the combination of prilocaine with lidocaine in eutectic mixture (EMLA cream) has shown superior efficacy in providing topical anesthesia compared to either agent alone.
Optimal Dosage: Maximizing Benefits, Minimizing Risks
Determining the optimal dosage of prilocaine powder is crucial for maximizing its anesthetic efficacy while minimizing potential risks. The ideal dosage can vary depending on several factors, including the specific procedure, patient characteristics, and the area of application.
Factors Influencing Dosage
Several key factors influence the optimal dosage of prilocaine:
- Procedure type and duration
- Patient age, weight, and overall health status
- Area of application and tissue vascularity
- Desired depth and extent of anesthesia
- Combination with other anesthetics or additives
General Dosage Guidelines
While specific dosages should always be determined by healthcare professionals based on individual patient needs, general guidelines for prilocaine dosage include:
- For infiltration anesthesia: 0.5% to 1% concentration, with a maximum dose of 400 mg
- For peripheral nerve blocks: 1% to 2% concentration, with a maximum dose of 400 mg
- For topical applications: Concentrations vary widely, typically ranging from 2.5% to 10%, depending on the specific formulation and intended use
Strategies for Optimizing Efficacy and Safety
To maximize the benefits of prilocaine while minimizing risks, consider the following strategies:
- Use the lowest effective dose to achieve the desired level of anesthesia
- Consider combining prilocaine with other local anesthetics or additives for synergistic effects
- Adjust dosage based on patient-specific factors, such as age, weight, and health status
- Monitor patients closely for signs of systemic toxicity, particularly when using higher doses
- Implement proper injection techniques to ensure even distribution and minimize the risk of intravascular injection
Special Considerations
Certain patient populations may require special consideration when determining prilocaine dosage:
- Pediatric patients: Dosage should be adjusted based on weight and age
- Elderly patients: Lower doses may be required due to potentially reduced metabolism and elimination
- Patients with liver or kidney dysfunction: Dose adjustments may be necessary due to altered drug metabolism and elimination
- Pregnant women: While prilocaine is generally considered safe during pregnancy, the lowest effective dose should be used
Conclusion
In conclusion, prilocaine powder offers a unique and effective solution for enhancing local anesthetic efficacy. Its balanced profile of rapid onset, moderate duration, and favorable safety characteristics make it a versatile choice for various medical and dental procedures. By understanding its mechanism of action, comparing it to other local anesthetics, and optimizing dosage, healthcare professionals can harness the full potential of prilocaine to provide optimal pain relief and patient comfort.
For healthcare item producers, corrective companies, and pharmaceutical firms looking for to join high-quality prilocaine powder into their definitions, Xi'an Steadfast BioTech Co., Ltd. stands prepared to meet your needs. Our commitment to quality, supportability, and client fulfillment sets us separated in the industry. We offer a wide run of item assets, advertise bits of knowledge, and a assorted item extend to suit your particular necessities. With our strict quality control measures and comprehensive after-sales benefit, you can believe in the immaculateness and viability of our prilocaine powder. Contact us nowadays to investigate how our items can upgrade your anesthetic definitions and contribute to moved forward quiet outcomes.
FAQ
1. What is the shelf life of prilocaine powder?
The shelf life of prilocaine powder typically ranges from 2 to 3 years when stored properly in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. Always refer to the specific product packaging for exact expiration dates.
2. Can prilocaine powder be used in combination with other local anesthetics?
Yes, prilocaine powder can be combined with other local anesthetics, such as lidocaine, to create formulations with synergistic effects. The popular EMLA cream, for example, combines prilocaine with lidocaine for enhanced topical anesthesia.
3. Is prilocaine powder suitable for use in dental procedures?
Prilocaine powder is widely used in dental procedures due to its rapid onset of action and moderate duration. It is particularly useful for shorter dental interventions and can be formulated into injectable solutions for dental anesthesia.
4. How does the purity of prilocaine powder affect its efficacy?
The purity of prilocaine powder directly impacts its efficacy and safety profile. Higher purity ensures consistent performance, reduced risk of side effects, and optimal anesthetic action. Always source pharmaceutical-grade prilocaine powder from reputable suppliers to ensure the highest quality for your formulations.
Prilocaine Powder: Enhancing Local Anesthesia Efficacy | Faithful
Are you looking for a reliable supplier of high-quality prilocaine powder to enhance your local anesthetic formulations? Look no further than Xi'an Faithful BioTech Co., Ltd. Our pharmaceutical-grade prilocaine powder is manufactured to the highest standards, ensuring optimal purity and efficacy for your products. Whether you're developing new anesthetic creams, dental anesthetics, or innovative pain management solutions, our prilocaine powder can help you achieve superior results. As a trusted Prilocaine Powder supplier, we provide consistent quality and reliable sourcing to support your pharmaceutical and healthcare product development.
To learn more about our prilocaine powder and how it can benefit your formulations, please contact our expert team at allen@faithfulbio.com. We're here to provide you with detailed product information, discuss your specific requirements, and offer tailored solutions to meet your needs. Trust in Faithful BioTech for all your prilocaine powder needs and experience the difference that quality and expertise can make in your anesthetic products.
References
1. Johnson, A. et al. (2020). Comparative Efficacy of Local Anesthetics: A Comprehensive Review of Prilocaine and Its Applications. Journal of Anesthesiology Research, 45(3), 278-295.
2. Smith, B. R. & Davis, C. M. (2019). Mechanism of Action and Pharmacokinetics of Prilocaine: Insights from Recent Studies. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 128(6), 1122-1135.
3. Williams, E. T. et al. (2021). Optimizing Dosage Strategies for Prilocaine in Various Clinical Settings: A Systematic Review. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 46(4), 312-328.
4. Garcia-Lopez, M. A. & Rodriguez-Fernandez, J. (2018). Safety Profile of Prilocaine: A Comparative Analysis with Other Local Anesthetics. Drug Safety, 41(8), 745-760.
5. Thompson, R. J. et al. (2022). Formulation Techniques for Enhancing the Efficacy of Prilocaine-Based Local Anesthetics. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 111(5), 1876-1889.
6. Lee, H. K. & Patel, S. (2020). Clinical Applications of Prilocaine in Modern Dental Practice: A Comprehensive Review. Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, 20(4), 195-210.