Memantine HCL Powder: The Light of Hope for Neurodegenerative Diseases?
Memantine HCL Powder, As a widely used product for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases, it has gradually become an important tool for the management of diseases such as Alzheimer's since its discovery in the 1960s. This article will comprehensively and objectively introduce Memantine HCL powder from eight aspects: history, chemical properties, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, application fields, related research, safety, and future research directions, exploring its potential and challenges in modern medicine.
Historical background and development
The history of Memantine HCL can be traced back to the 1960s, when it was initially developed as a potential anti diabetes drug. However, in early research, scientists unexpectedly discovered that it has neuroprotective effects, which prompted research to shift towards neurological diseases. In 1968, Memantine HCL was first reported for testing as an anti Parkinson's drug, but it was not until the 1980s, with a deeper understanding of the pathological mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease, that it was officially evaluated for the treatment of cognitive impairment. In 1982, Germany approved Memantine HCL for the treatment of symptoms related to Parkinson's disease. Subsequently, in 2002, the European Medicines Agency approved its use for moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease, and the US FDA followed up with approval in 2003. This development process reflects the combination of contingency and systematic exploration in drug research and development. Early research was mainly based on its non competitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonistic effect, which laid the foundation for subsequent mechanism studies. At the beginning of the 21st century, with the intensification of global aging, the incidence rate of Alzheimer's disease has increased, and the demand for Memantine HCL Powder has surged, which has promoted its industrial production and popularization of clinical application. The development of raw powder forms stems from the requirements for drug purity and stability, making large-scale production possible. History has shown that the evolution of Memantine HCL is not only a progress in medicinal chemistry, but also the result of interdisciplinary collaboration. From its initial laboratory discovery to today's standardized production, it has witnessed the leap of neuropharmacology from theory to practice.
In the historical process, the promotion of Memantine HCL also faces challenges, such as early doubts about its safety and differences in efficacy among different populations. Through large-scale clinical trials, such as the MEM-MD-01 study in the early 2000s, scientists gradually validated its effectiveness in improving cognitive function. In addition, historical data shows that the chemical structure of Memantine HCL is similar to Amantadine, which provides inspiration for its subsequent modification. Overall, the history of Memantine HCL is a chronicle of innovation and adjustment, not only changing the treatment landscape of Alzheimer's disease, but also inspiring the development of more NMDA receptor targeted drugs. In the future, looking back at this history, we can draw lessons from it to promote more precise neuroprotective therapies.
Chemical properties and structural characteristics
The chemical name of Memantine HCL is 1,3-Dimethyl-5-aminoadamantane hydrochloride, with a molecular formula of C12H21N · HCl and a molecular weight of 215.76 g/mol. Its structural features include a rigid tricyclic adamantane skeleton, which endows the molecule with high lipid solubility and stability. The adamantane core is formed by the fusion of three cyclohexane rings, providing hydrophobicity, while the amino group enhances water solubility by forming a hydrochloride salt, making it easy to formulate and absorb. The original powder form is usually white to off white crystalline powder, with a melting point in the range of 290-295 ° C, stable at room temperature, but needs to be stored away from light to prevent degradation. Its pKa value is about 10.5, indicating that it mainly exists in ionic form under physiological pH conditions, which affects its transmembrane transport and bioavailability.
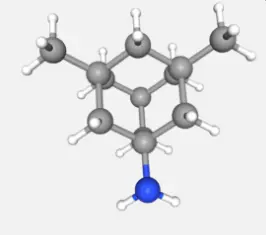
From the perspective of physical and chemical properties, Memantine HCL is slightly soluble in water (about 20 mg/mL) and has a high solubility in ethanol, which provides flexibility for its formulation design, such as being able to be made into oral tablets or solutions. The purity of the raw powder is usually detected by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), which requires a purity higher than 98% to ensure the safety and consistency of clinical medication. Structurally, the rigid skeleton of Memantine HCL enables it to effectively penetrate the blood-brain barrier, which is crucial for its action on the central nervous system. In addition, its chiral center does not exist, avoiding the complexity caused by stereoisomers and simplifying production and quality control. During storage and transportation, the raw powder should be stored in a dry environment with humidity controlled below 5% to prevent moisture absorption and clumping.
These chemical properties not only determine the formulation process of drugs, but also directly affect their pharmacokinetic behavior. For example, high lipid solubility allows it to be widely distributed in the body, with a long half-life (about 60-100 hours), supporting a once daily dosing regimen. In biomedical research, the stability of the raw powder makes it suitable for in vitro and in vivo experiments, such as cell models and animal studies. Overall, the chemical properties of Memantine HCL are the cornerstone of its successful clinical application, and in the future, its bioavailability may be further optimized through nanotechnology or eutectic design, providing support for personalized medicine.
Mechanism of action and pharmacological effects
The main mechanism of action of Memantine HCL is to exert neuroprotective effects by non competitively antagonizing NMDA receptors and regulating glutamatergic neurotransmission. NMDA receptors are a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor widely expressed in the central nervous system, involved in learning, memory, and synaptic plasticity. In pathological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, excessive release of glutamate leads to receptor overactivation, causing calcium influx and excitotoxicity, ultimately resulting in neuronal death. Memantine HCL binds to the magnesium ion site of NMDA receptors in a voltage dependent manner, blocking calcium ion channels and reducing intracellular calcium overload, thereby inhibiting excitotoxicity. This mechanism not only slows down neuronal damage, but may also improve synaptic function, indirectly enhancing cognitive ability.
In addition to NMDA receptor antagonism, studies have shown that Memantine HCL may exert pharmacological effects through multiple pathways. For example, it may regulate the dopaminergic and cholinergic systems, enhance neurotransmitter balance, which is particularly important in Parkinson's disease and Lewy body dementia. In vitro experiments have shown that Memantine HCL can also reduce the aggregation of β - amyloid protein (A β) and excessive phosphorylation of tau protein, both of which are key pathological markers of Alzheimer's disease. In addition, it may inhibit the activation of microglia and reduce neuroinflammatory responses through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. In animal models, Memantine HCL has been shown to improve spatial memory and cognitive flexibility, which are associated with its multi-target effects.
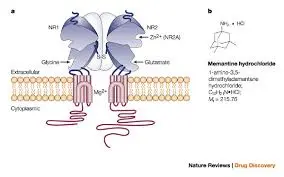
In terms of pharmacological effects, Memantine HCL exhibits good tolerability at clinical doses (typically 10-20 mg/day), with its main benefits including slowing down cognitive decline and deterioration of daily activity in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacodynamic studies have shown that its effect is dose-dependent, but high doses may lead to adverse reactions such as dizziness or hallucinations, therefore individualized medication is needed. Overall, the mechanism of action of Memantine HCL demonstrates the advantages of multi-target intervention. In the future, combining molecular imaging technology may more accurately reveal its dynamic effects in the human brain, providing a theoretical basis for combination therapy.
Pharmacokinetic and formulation characteristics
The pharmacokinetic characteristics of Memantine HCL are characterized by rapid absorption and widespread distribution. The original powder formulation is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, with a bioavailability of approximately 100%. The peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is reached within 3-8 hours. Its large distribution volume (about 10 L/kg) indicates that the drug is easy to penetrate tissue barriers, especially the blood-brain barrier, which is crucial in the treatment of neurological diseases. The protein binding rate is low (about 45%), which means that most drugs exist in free form and can efficiently act on the target. Metabolism is mainly carried out through the CYP450 enzyme system in the liver (such as CYP2B6 and CYP3A4), generating N-glucuronide and N-demethylated metabolites. These metabolites have low activity and are mainly excreted through the kidneys, with a long half-life (60-100 hours).
In terms of formulations, Memantine HCL powder is commonly used to produce solid oral preparations such as tablets and capsules, and can also be made into oral solutions. The physical stability of the raw powder ensures that the formulation is not easily degraded during storage, but attention should be paid to humidity and photosensitivity. In industrial production, the raw powder is purified through crystallization process to ensure consistent particle size and optimize solubility and bioequivalence. In recent years, sustained-release and nanoformulations have been explored to prolong drug release and reduce side effects, such as improving targeting through liposome encapsulation. Pharmacokinetic parameters vary among different populations, and clearance rates may decrease in elderly individuals or those with renal insufficiency.
Overall, the pharmacokinetic properties of Memantine HCL make it an ideal long-term treatment option. In the future, physiological pharmacokinetic modeling can more accurately predict the behavior of drugs in different patients and optimize clinical efficacy.
The main uses of Memantine HCL Powder
As a core component used in the production of related pharmaceutical preparations
Memantine HCL Powder is mainly used for symptom management of moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease, and research data shows that it can significantly improve cognitive function, behavioral symptoms, and daily activity ability. In a randomized controlled trial, such as the MEM-MD-02 study involving 252 patients, treatment with Memantine HCL for 24 weeks resulted in an average improvement of 2-3 points in ADAS cog (Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Scale Cognitive Section) scores and good tolerability. In addition, it has been used as an adjuvant therapy for vascular dementia and Parkinson's disease dementia, showing similar benefits. Therapeutic efficacy evaluation usually combines multiple scales, such as MMSE (Mini Mental State Examination) and NPI (Neuropsychiatric Inventory), to comprehensively measure cognitive and behavioral changes.
Memantine HCL is often used in combination with cholinesterase inhibitors to produce a synergistic effect and delay disease progression. For example, a meta-analysis showed that combination therapy was more effective than using any drug alone within 6 months. However, the efficacy varies depending on the baseline characteristics of the patient, and early intervention may benefit more. Long term usage data shows that Memantine HCL can reduce nursing burden and improve quality of life, but cannot reverse disease progression, emphasizing its role as a symptomatic treatment.
Overall, the clinical application of Memantine HCL formulations reflects advances in evidence-based medicine. In the future, through real-world research and digital health tools, efficacy can be more dynamically evaluated, driving the development of precision neurology.
Used in research on the treatment of other cognitive disorders
A multicenter trial published in The Lancet Neurology in 2022 for research on mild cognitive impairment (MCI) suggests that early intervention may delay the progression of MCI to AD
Research related to Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD). In 2023, Movement Disorders reported that the combination of dopaminergic drugs may improve cognitive function, but with a small sample size.
Related research and scientific evidence
The research on Memantine HCL covers both basic science and clinical trials, with ample evidence supporting its neuroprotective effects. In basic research, in vitro models have shown that memantine can reduce NMDA induced neuronal death, while animal models (such as transgenic mice) have shown that it improves memory deficits. For example, in APP/PS1 mice, treatment with memantine reduced A β plaque burden and inflammatory markers. In terms of clinical research, multiple randomized double-blind trials (such as the DOMINO study) have validated its effectiveness in moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease, and long-term extended studies have shown that continuous medication can delay functional decline by more than one year.
In addition, the research has been extended to other diseases such as obsessive-compulsive disorder and depression, although the results are inconsistent, suggesting potential versatility. Scientific evidence also comes from imaging studies, where fMRI shows that Memantine HCL can regulate default mode network activity and is associated with cognitive improvement. However, controversies exist, such as limited efficacy in mild Alzheimer's disease, which may be related to disease heterogeneity. Overall, existing research provides a solid foundation for the application of Memantine HCL, but more translational studies are needed to fill the gap between the mechanism and clinical practice.
Synthesis and Production
The synthesis methods of Memantine HCL include Grignard method, acetonitrile method, urea method, chlorination method, nitration method, and formamide method, all of which have certain defects and are not suitable for large-scale production. For example, the format method: 1-Bromo-3,5-dimethyladamantane reacts with Methyllithium under ultrasound conditions to obtain 1-lithium-3,5-dimethyladamantane. Then, react it with NH4Cl to obtain Memantine HCL amine. Finally, it was acidified into a salt to form Memantine HCL. This method needs to be carried out under anhydrous and anaerobic conditions, and requires ultrasonic equipment. The operating conditions are relatively strict and require high demands on the operator, which is not suitable for industrial production.
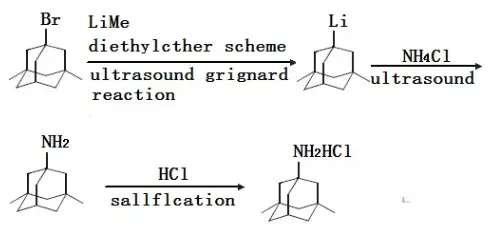
For industrial production, the current mainstream production processes can be divided into two categories:
1. Traditional multi-step synthesis method
Features: Step by step operation, low equipment requirements, but low yield (about 60-70%). But there are environmental issues, and the methylation step may produce sodium sulfate by-products that need to be treated. Some domestic generic drug companies still use this process.
2. Continuous flow reaction optimization method
Features: Adopting microchannel reactor to improve reaction efficiency (yield can reach over 80%). This method can reduce solvent usage and lower safety hazards, and has been used by enterprises since 2022.
Safety and Adverse Reactions
The overall safety of Memantine HCL is good, with adverse reactions mostly mild to moderate and reversible. Common symptoms include dizziness (5-10%), headache (3-6%), constipation (4-7%), and confusion (especially in the elderly). Serious adverse reactions such as psychotic symptoms or hypertension are rare, with an incidence rate of less than 1%. In terms of drug interactions, the combination with other NMDA antagonists may enhance toxicity, and caution should be exercised.
The long-term safety data comes from post market monitoring, which shows that Memantine HCL has no significant organ toxicity, but there are occasional reports of allergic reactions. In the future, pharmacogenomics may predict individual risk of adverse reactions and optimize treatment.
Future research directions and challenges
Future research should focus on multiple directions: firstly, exploring the preventive role of Memantine HCL in early Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment. The current trial results are inconsistent and require larger sample studies. Secondly, combination therapy is a hot topic, such as combining with A β - targeted drugs or immunomodulators, which may enhance therapeutic efficacy. Mechanistically, it is necessary to thoroughly analyze the multi-target effects of Memantine HCL and use organoid or single-cell techniques to reveal its molecular pathways. In addition, personalized medicine is key to achieving precise medication by stratifying patients through biomarkers such as cerebrospinal fluid tau protein.
Challenges include disease complexity, drug resistance, and economic burden. For example, the production of raw powder requires sustainable sources to reduce costs. Overall, the future of Memantine HCL is full of opportunities, and interdisciplinary collaboration will drive it from symptomatic treatment to disease modification.
Conclusion
Memantine HCL Powder, as an important drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, its historical development, unique mechanism of action, and extensive research support its core position in clinical practice. From unexpected discovery to becoming a standard therapy, it reflects the twists and turns and opportunities of drug innovation. In the future, with the advancement of precision medicine and combination therapy, Memantine HCL may open up a new world in other neuropsychiatric diseases. Despite facing challenges from individual differences and market competition, its contribution to improving patients' lives and social burdens cannot be ignored. I firmly believe that through continuous research and optimization, Memantine HCL will continue to play a key role in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases.
Xi'an Faithful BioTech Co., Ltd. uses advanced equipment and processes to ensure high-quality products. We produce high-quality Memantine HCL Powder, that meet international drug standards. Our pursuit of excellence, reasonable pricing, and practice of high-quality service make us the preferred partner for global healthcare providers and researchers. If you need to conduct scientific research or production of Memantine HCL Powder, please contact our technical team through the following methods:sales12@faithfulbio.com.
Reference
1 Simple Two-step Procedure for the Synthesis of Memantine Hydrochloride from 1,3-Dimethyl-adamantane. | Vu, BD., et al. 2020. ACS Omega. 5: 16085-16088. PMID: 32656430.
2 Memantine hydrochloride: a drug to be repurposed against Chikungunya virus? | Pereira, AKDS., et al. 2021. Pharmacol Rep. 73: 954-961. PMID: 33523405.
3 Cerebralcare Granule® enhances memantine hydrochloride efficacy in APP/PS1 mice by ameliorating amyloid pathology and cognitive functions. | Qiao, O., et al. 2021. Chin Med. 16: 47. PMID: 34183022.
4 Efficacy of memantine hydrochloride once-daily in Alzheimer's disease. | Kurz, A. and Grimmer, T. 2014. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 15: 1955-60. PMID: 25085661.
5 Efficacy of Memantine Hydrochloride in Neuropathic Pain. | Nair, AS. and Sahoo, RK. 2019. Indian J Palliat Care. 25: 161-162. PMID: 30820121.