Misoprostol Powder: How does this' molecular key 'open multiple doors to modern medicine?
In the treasure trove of medicinal chemistry, Misoprostol powder is like a cleverly designed 'molecular key'. Although its appearance is not stunning - a white to off white crystalline powder, its unique molecular structure endows it with the magical ability to open multiple biological locks such as gastrointestinal protection, induction of labor, hemostasis, and lifesaving. As pharmaceutical raw material experts, we not only view it as an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), but also as a classic case that demonstrates how to unlock its broad potential in the field of human health through a deep understanding of a molecule's structure. Let's start from the molecular level and delve deeper into the mystery of this' key '.
Structural Features - A Carefully Carved 'Molecular Key'
The chemical charm of Misoprostol begins with its intricate and unique molecular framework. Its core is a ProstaglandinE1 (PGE1) analogue, chemically named (11 α, 13E) -11,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprostate-13-en-1-oic acid methyl ester. This seemingly obscure name actually accurately depicts every key tooth mark of it as a 'key'.
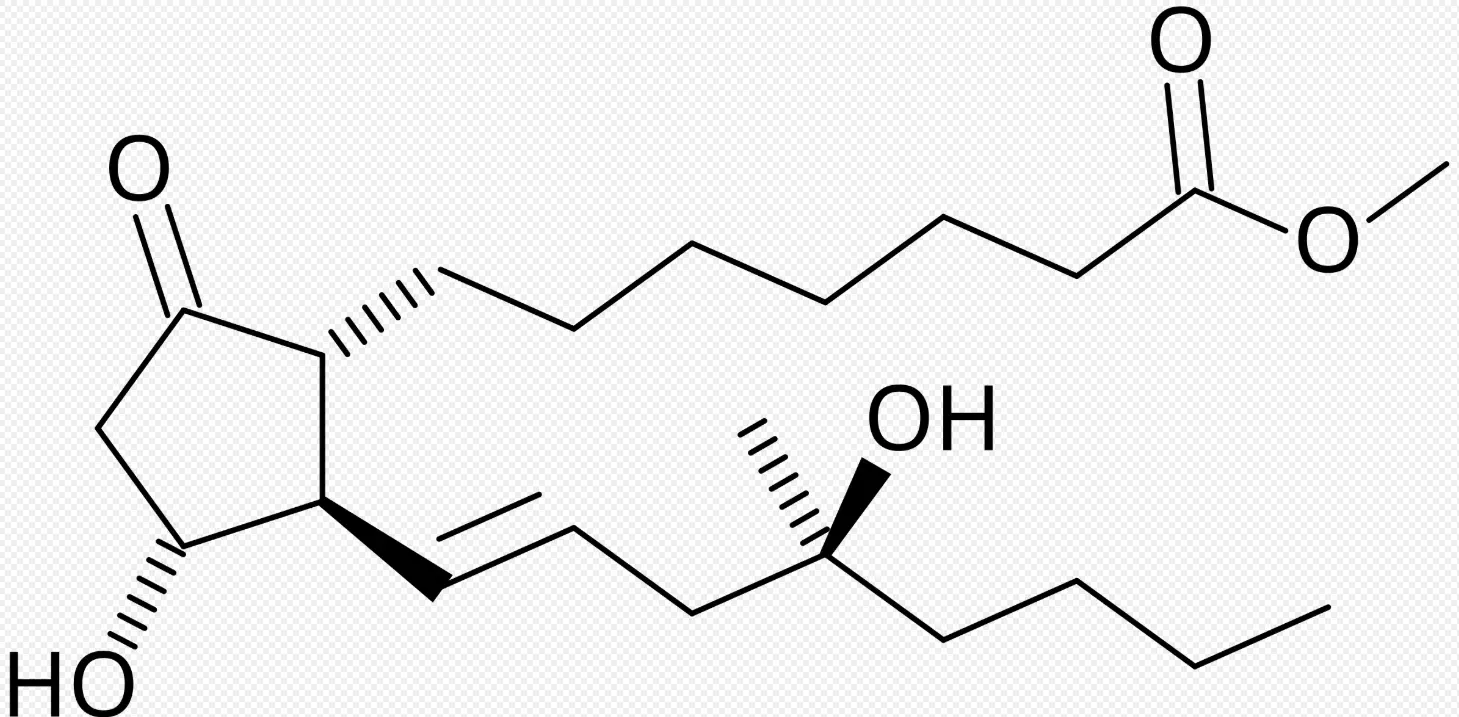
Firstly, its molecular core is a 20 carbon carboxylic acid backbone, which is a characteristic of classical Prostaglandin. But Misoprostol powder is not a simple replica of natural Prostaglandin. The most critical modification in its structure is at the C-16 position. Natural PGE1 is a hydrogen atom at this position, while Misoprostol introduces a methyl group (- CH3) and a hydroxyl group (- OH). This seemingly minor change is the finishing touch of the entire molecular design. It greatly enhances the oral bioavailability of Misoprostol. After oral administration, natural Prostaglandin is heavily metabolized and inactivated upon its first passage through the liver (with a strong first pass effect). The methylation of C-16 acts as a "shield" that effectively resists the rapid attack of liver enzymes, allowing oral Misoprostol to have sufficient "force" to enter the systemic circulation and exert its effects. A pharmacokinetic study showed that the bioavailability of oral Misoprostol was significantly higher than that of natural PGE1, directly attributed to this structural modification.
Secondly, the three key chiral centers (C-11, C-12, and C-15) and one key C-13 trans double bond in the molecule together form a three-dimensional configuration that precisely matches the "keyhole" of the Prostaglandin receptor (EP receptor) in vivo. Especially the hydroxyl group at C-15 position is an essential group for activating receptors. If the stereochemical configuration changes, its pharmacological activity will sharply decrease or even completely lose. This is like the teeth marks of a key must correspond precisely, and a slight deviation will prevent unlocking. In the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, stereoselective synthesis and high-purity control (usually requiring chemical purity>99.0% and single impurity<0.1%) are the technical cores to ensure that each batch of raw powder has consistent and efficient "unlocking" ability. Modern synthetic techniques, such as asymmetric catalysis or enzymatic methods, can efficiently and environmentally construct these chiral centers.
In addition, Misoprostol molecules have amphiphilicity: the methyl carboxylate moiety gives them a certain lipophilicity, while multiple hydroxyl groups provide hydrophilicity. This property enables it to penetrate the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane, interact with G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) located on the cell membrane, and efficiently initiate intracellular signaling.
Therefore, from the perspective of raw materials, Misoprostol powder is not a simple chemical intermediate. It is a paradigm of structure-activity relationship (SAR) research, where the arrangement of each atom and group has been carefully designed and validated, together creating this efficient, stable, and orally accessible 'molecular master key'. Every step of its synthesis and purification is a tribute and reproduction of the precise structure of the molecule.
Application areas - from gastric mucosal defender to versatile obstetrician
The application history of Misoprostol powder is an excellent textbook on the new use of old drugs. Its initial approved use demonstrated its role as a "guardian of the gastric mucosa", while subsequent expanded applications revealed its enormous potential as a "versatile obstetrics" and "hemostatic pioneer".
1. The cornerstone of gastrointestinal protection:
In the 1980s, Misoprostol powder was developed for the prevention and treatment of gastric ulcers and mucosal damage caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as acetylsalicylic acid and Ibuprofen. NSAIDs reduce the synthesis of Prostaglandin, which protects the gastric mucosa, by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX). Misoprostol powder, as an exogenous Prostaglandin analogue, directly supplements this protective substance. A large, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study (MUCOSA trial) showed that for arthritis patients taking NSAIDs, simultaneous oral administration of Misoprostol can reduce the risk of severe upper gastrointestinal complications such as bleeding and perforation by about 40%. Although proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have become first-line choices due to their better tolerance (with fewer side effects such as diarrhea), Misoprostol remains an important alternative for preventing NSAIDs related gastric mucosal injury, especially for patients who require strong mucosal protection and cannot use PPIs.
2. Revolutionary drugs in the field of obstetrics:
This is the most widely used and influential field of Misoprostol powder. With its stability, room temperature storage, low cost, and diverse administration methods (oral, sublingual, buccal mucosal, vaginal), it has become a pillar of obstetric care in resource limited areas worldwide.
Induced abortion and cervical ripening promotion: For pregnant women who require induced abortion in their first month of pregnancy, Misoprostol can effectively soften and dilate the cervix, inducing uterine contractions. The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines recommend that low-dose Misoprostol is a safe and effective option for induced abortion. Compared to traditional oxytocin, it is more effective when the cervix is immature.
Treatment and prevention of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH): PPH is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. Misoprostol powder can cause strong uterine contractions and is a life-saving medication for preventing and treating PPH. The latest results of a multicenter randomized controlled trial (E-MOTIVE trial) conducted in Africa and Asia indicate that early intervention based on Misoprostol can significantly reduce the incidence of severe postpartum hemorrhage.
Miscarriage management: The sequential use of Misoprostol powder and Mifepristone is a recommended standard protocol for medical abortion (early and mid pregnancy) by the World Health Organization. Misoprostol alone is also used to treat incomplete abortion and missed abortion, avoiding surgical risks.
3. Other exploratory applications:
This also includes the use of mifepristone in combination for cervical pre-treatment before gynecological surgery, as well as exploring its potential value in the treatment of gastroparesis and promoting wound healing.
Principle of action - precise activation of cellular signals by "microscopic messengers"
The reason why Misoprostol powder can serve multiple purposes is that as a Prostaglandin analogue, it can accurately mimic endogenous signaling molecules and "communicate" with the widely distributed Prostaglandin E receptor (EP receptor) family in the body. Its working principle is a precise cascade reaction that begins with cell membrane receptors.
1. Receptor targeting: One key unlocks multiple locks
Misoprostol is an agonist of EP receptors (mainly four subtypes: EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4), but its affinity for different subtypes varies, which determines its diverse physiological effects.
Misoprostol powder mainly acts on the smooth muscles of the uterus and gastrointestinal tract by stimulating EP2 and/or EP3 receptors. After activation, the receptor increases intracellular calcium ion concentration and reduces cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels (EP3 receptor) through the G protein signaling pathway, ultimately triggering strong smooth muscle contraction. This is the molecular basis for causing uterine contractions (used for induction of labor, hemostasis) and gastrointestinal smooth muscle contractions (leading to diarrhea side effects).
In gastric mucosal cells, activation of EP receptors (especially EP1 and EP4) can promote the secretion of bicarbonate and mucus from the gastric mucosa, enhancing the mucosal barrier; Simultaneously inhibit the secretion of gastric acid by gastric wall cells. This dual mechanism of "enhancing defense and weakening attack" constitutes its powerful protective effect on the gastric mucosa.
2. The 'domino effect' at the cellular and molecular levels
After the receptor is activated, a series of rapid signaling events occur within the cell. Taking uterine smooth muscle cells as an example: receptor activation → G protein dissociation → activation of phospholipase C (PLC) → production of inositol triphosphate (IP3) → IP3 triggers endoplasmic reticulum release of calcium ions → sudden increase in cytoplasmic calcium ion concentration → binding of calcium ions to calmodulin → activation of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) → phosphorylation of myosin → interaction between actin and myosin → cell contraction. This process is like toppling a series of dominoes, ultimately magnifying microscopic molecular binding events into visible organ level contractions.
3. Support for pharmacokinetics
Misoprostol powder is rapidly absorbed and extensively hydrolyzed by esterases in the body into its active metabolite, Misoprostol acid. This metabolite is the main form that truly binds to the EP receptor. The plasma half-life of Misoprostol acid is relatively short (about 20-40 minutes), but its pharmacological effects (such as uterine contractions) can last for several hours. The characteristic of "short drug replacement long efficacy" is related to the sustained activation of intracellular signaling pathways and receptor downregulation it triggers.
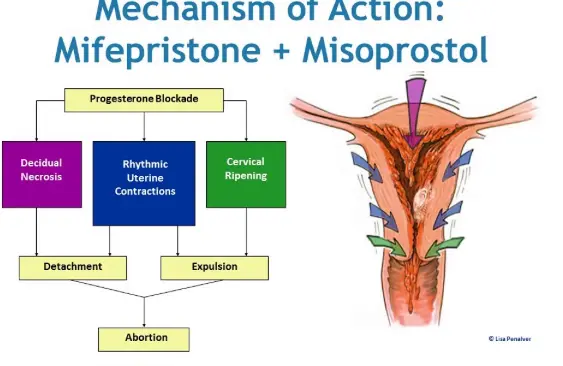
Research Direction - Beyond Classics, Expanding the Xinjiang Territory
Although Misoprostol is a mature drug, scientific exploration around its raw materials and applications has never stopped. The current research direction is developing in multiple dimensions, including optimizing delivery, expanding indications, improving tolerance, and exploring new treatment models.
1. Development of a new delivery system: aimed at improving targeting and reducing systemic side effects.
Local targeted delivery: research and develop special dosage forms (such as biodegradable implants or gel) for intrauterine or paracervical administration, so that the drug can reach a high concentration locally in the target organ, and minimize gastrointestinal side effects (such as diarrhea, abdominal pain) and systemic effects (such as fever, chills). A preclinical study developed a Misoprostol Powder intrauterine sustained release system based on thermosensitive hydrogel, which showed a more lasting and stable uterine contraction effect in animal models, and significantly reduced systemic exposure.
Improvement of oral formulations: Developing enteric coated or delayed release formulations to allow drugs to be released in the intestine rather than the stomach, in order to alleviate upper abdominal discomfort. Meanwhile, studying the effects of different crystal forms on solubility and bioavailability to optimize the onset time and effectiveness intensity.
2. Exploration of new indications:
Tissue repair and regeneration: Based on the role of Prostaglandin in promoting angiogenesis and epithelial repair, researchers are exploring the possibility of local application of Misoprostol Powder to promote the healing of chronic wounds such as diabetes foot ulcers and pressure ulcers. Early clinical trials have shown that local use of Misoprostol ointment can promote granulation tissue growth in refractory wounds.
Neuroprotection and inflammation regulation: EP2 and EP4 receptors play complex roles in central nervous system inflammation and injury. Some basic research is evaluating the neuroprotective potential of Misoprostol acid in models such as cerebral ischemia and Alzheimer's disease, but its clinical translation requires extreme caution and precise balancing of its benefits with potential vascular and inflammatory side effects.
Anti fibrotic therapy: Studies suggest that the Prostaglandin pathway may inhibit the fibrotic process in certain tissues, such as the lungs and liver. Whether Misoprostol can play a role in diseases such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is another frontier of exploration.
3. Compound preparations and combination therapy strategies:
Make Misoprostol powder into a fixed dose combination with drugs that complement other mechanisms to improve efficacy and convenience. For example, combining with more potent anti secretory drugs for complex gastric mucosal lesions; Or develop a combination drug package containing Misoprostol powder and Tranexamic Acid for postpartum hemorrhage prevention, which synergistically stops bleeding from the perspectives of uterine contractions and anti fibrinolysis.
These research directions indicate that the "old key" of Misoprostol powder is being re polished by modern technology in order to open more "new locks" to the realm of health. The in-depth study of its raw powder is the starting point of the entire value innovation.
Conclusion
The story of Misoprostol powder, from a "chemical shield" that protects the gastric mucosa to an "obstetric cornerstone" that saves countless mother and baby lives, is a vivid portrayal of how structure determines function and knowledge drives innovation in pharmaceutical science. As pharmaceutical raw material experts, what we see is not only a white powder, but also a smart molecular entity, a bridge connecting basic research and clinical needs, and a deep commitment to continuously contribute to global public health, especially maternal and child health in low - and middle-income areas. In the future, with breakthroughs in delivery technology and research on new indications, this classic "molecular key" will continue to shine its unique and indispensable light in the treasure trove of human disease resistance.
Xi'an Faithful BioTech Co., Ltd. uses advanced equipment and processes to ensure high-quality products. We produce high-quality raw Misoprostol powder that meet international drug standards. Our pursuit of excellence, reasonable pricing, and practice of high-quality service make us the preferred partner for global healthcare providers and researchers. If you need to conduct scientific research or production of Misoprostol , please contact our technical team through the following methods sales1@faithfulbio.com.
Reference
1. Allen, R., O'Brien, B. M., & Chien, P. F. (2009). Uses of misoprostol in obstetrics and gynecology. Reviews in Gynaecological and Perinatal Practice, 6(3-4), 142-148.
2. Goldberg, A. B., Greenberg, M. B., & Darney, P. D. (2001). Misoprostol and pregnancy. New England Journal of Medicine, 344(1), 38-47.
3. Silver, R. M., & Wolfe, H. M. (2012). Pharmacologic management of postpartum hemorrhage. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology, 55(1), 218-227.
4. Tang, O. S., & Ho, P. C. (2006). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of misoprostol. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology, 2(4), 539-549.