Peptide MT2 Powder:How did it become a revolutionary peptide compound in the field of pharmaceutical raw materials?
In the vast world of pharmaceutical raw materials, Melanotan II (MT2) is like a rising star, attracting the attention of countless researchers and industry experts with its unique peptide structure and multifunctional applications. Imagine a compound originally designed for tanning the skin unexpectedly demonstrating potential in the fields of weight loss, sexual dysfunction treatment, and even neuroprotection, which makes one marvel at the wonders and unpredictability of science. The story of Peptide MT2 Powder began in the 1980s, when a research team at the University of Arizona was dedicated to developing a synthetic peptide to mimic the naturally occurring alpha melanocyte stimulating hormone (alpha MSH) in the human body, with the aim of helping people achieve healthy bronze colored skin without exposure to harmful ultraviolet radiation. However, as research deepened, scientists discovered that the effect of this compound goes far beyond that - it activates melanocortin receptors, triggering a series of chain reactions in the human body, from appetite regulation to increased libido, and possibly anti-inflammatory effects, gradually uncovering the mystery of MT2. In this introduction, we will delve into Peptide MT2 Powder and take you on a journey to appreciate the charm of this molecular miracle.
Development History
The development history of Peptide MT2 Powder is a legend full of unexpected discoveries and scientific breakthroughs, perfectly interpreting the crucial role of "contingency" in drug development. The story begins in the early 1980s, when a research team from the University of Arizona in the United States began studying the Melanocortin system. Their original intention was to develop a synthetic analog that can simulate alpha MSH for the treatment of skin diseases such as photosensitive dermatitis, and to help people achieve tanning effects without increasing the risk of skin cancer. Alpha MSH is a naturally occurring peptide hormone that promotes melanin production by activating melanocortin receptor 1 (MC1R), thereby protecting the skin from UV damage. However, early research soon encountered challenges: α - MSH itself has a very short half-life in vivo and low oral bioavailability, making it difficult to apply in practice. To address these issues, researchers have designed MT2 through peptide modification techniques - a cyclic heptapeptide with a structure similar to alpha MSH, but significantly improved its stability and receptor affinity by introducing specific amino acid substitutions (such as replacing Asp with Nle) and cyclization structures.
In preliminary animal experiments, MT2 demonstrated astonishing effects: it not only effectively induced melanin production, but also unexpectedly observed side effects of weight loss and enhanced sexual behavior. This discovery quickly pushed research towards new directions. In the 1990s, MT2 entered the clinical trial phase, initially focusing on dermatological applications such as testing as a "tanning injection". However, as more data accumulates, scientists realize that its potential goes far beyond that. For example, in the early 2000s, a study on obese patients showed that MT2 could significantly reduce weight by regulating appetite, which sparked interest in the treatment of metabolic diseases in the pharmaceutical industry. At the same time, researchers in the field of sexual medicine have begun to explore its application in the treatment of sexual dysfunction, particularly in women with decreased libido disorder (HSDD) and men with erectile dysfunction. It quickly became popular in both academic and commercial fields as a research chemical and raw powder.
A key turning point in the development process is the rise of the Internet and social media, which has promoted the popularity of MT2 in non-medical uses. Many fitness enthusiasts and beauty consumers have started using this raw powder on their own in pursuit of quick tanning or weight loss effects, but this also brings safety concerns, such as the possibility of adverse reactions caused by unpurified products. From the perspective of pharmaceutical raw material specialization, the development of MT2 highlights the complex path of peptide drugs from laboratory to market: it requires multidisciplinary collaboration, including chemical synthesis, pharmacological testing, and clinical validation. Today, MT2 raw powder has become an important component of the global pharmaceutical raw material supply chain, with suppliers ensuring its purity and quality through GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards, while promoting legitimate research. Looking back on this journey, we not only see the power of scientific innovation, but also realize the importance of regulatory and ethical challenges. The story of MT2 reminds us that drug development is often a winding path full of unknown surprises and risks.
Characteristics of Peptide MT2 Powder
MT2, as a pharmaceutical raw material powder, has unique characteristics among peptide compounds. These characteristics not only determine its pharmacological effects, but also affect its performance in production and application. From a chemical structure perspective, MT2 is a synthetic peptide composed of seven amino acids (Ac-Nle-cyclo [Asp-His-D-Phe-Arg-Trp-Lys] - NH2). Its cyclic structure is formed through side chain bonding, which endows it with excellent stability and resistance to enzymatic hydrolysis. Compared to linear peptides, this cyclic design significantly prolongs its half-life in vivo, reaching several hours, while the half-life of natural alpha MSH is only a few minutes. This allows MT2 to continue to function, reducing the frequency of administration and improving patient compliance. In terms of physical properties, high-purity MT2 raw powder usually appears as a white to off white powder, easily soluble in water or physiological saline, forming a colorless solution, which facilitates the preparation of formulations. However, its solubility is greatly affected by pH value and may be unstable in acidic environments. Therefore, strict control conditions such as avoiding light, low temperature (2-8 ° C), and dry environment are required during storage to prevent degradation and oxidation.
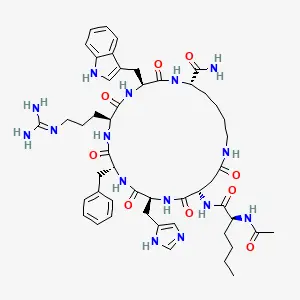
From the analysis of pharmacokinetic characteristics, MT2 has a high bioavailability, which is attributed to its peptide structure's high affinity for melanocortin receptors. Its distribution volume is relatively small, mainly concentrated in peripheral tissues such as skin, brain, and reproductive organs, which explains its pleiotropy. Metabolism is mainly carried out through peptidases in the kidneys and liver, producing inactive amino acids that are ultimately excreted in urine with low overall toxicity. Interestingly, there is another little-known aspect of MT2's characteristics: its "polymorphism". Under different crystallization conditions, this raw powder may form multiple crystal forms, each with slight differences in dissolution rate and stability, providing optimization space for pharmaceutical formulation engineers, such as enhancing its targeting through nanotechnology.
As a pharmaceutical raw material, the quality standards of MT2 powder are crucial. High purity products (usually ≥ 98%) need to be validated through techniques such as HPLC, mass spectrometry, and NMR to ensure the absence of impurities such as residual solvents or related peptides. In addition, its characteristics also include a certain degree of moisture absorption, which means that it is easy to absorb moisture in humid environments, leading to clumping or reduced potency. Therefore, the packaging must use sealed containers and add desiccants. From an application perspective, these features make MT2 highly favored in personalized medicine: doctors or researchers can flexibly adjust dosage and formulation according to patient needs.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of MT2 is a fascinating molecular dance that orchestrates a series of physiological responses in the human body by precisely targeting melanocortin receptors (MCRs). The melanocortin receptor belongs to the G protein coupled receptor (GPCRs) family, which includes five subtypes (MC1R to MC5R) and is distributed in different tissues and organs. MT2, as a non selective agonist, has affinity for these receptors, but particularly prefers MC1R, MC3R, MC4R, and MC5R, with MC4R activation being the core of most of its key effects. When MT2 is absorbed into the bloodstream, it binds to these receptors and triggers intracellular signaling pathways, mainly including activating Adenylate cyclase, increasing levels of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), and thereby regulating gene expression and cellular function.
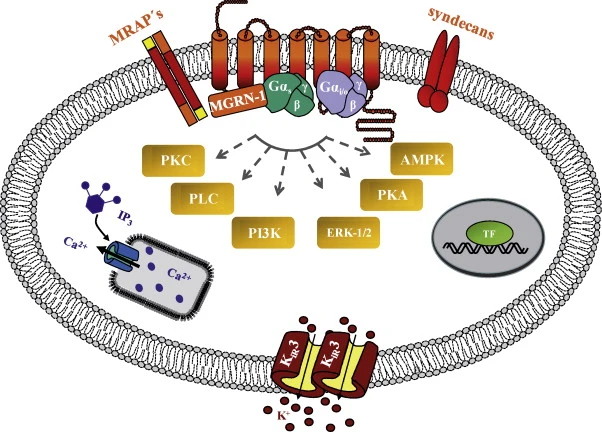
Taking skin tanning as an example, when MT2 binds to MC1R, it simulates the action of α - MSH, stimulating melanocytes to produce more melanin - a natural pigment that can absorb ultraviolet light and protect the skin from DNA damage. This not only explains its initial design purpose, but also reveals its potential in preventing skin cancer. More interestingly, the activation of MC4R by MT2 is key to its weight loss and sexual function enhancement effects. MC4R is widely expressed in the hypothalamus, which is the center of the brain to regulate appetite and energy balance. When MT2 activates these receptors, it inhibits the release of neuropeptide Y (NPY) - a potent appetite stimulating factor - while promoting the secretion of melanocortin related hormones such as alpha MSH, resulting in a sense of fullness and reduced food intake. In animal models, mice given MT2 showed significant weight loss within a few weeks without affecting muscle mass, providing a new approach for obesity treatment.
In terms of sexual function, the mechanism of action of MT2 involves coordination among multiple brain regions. By activating MC4R, it enhances the dopaminergic pathway - dopamine is a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and motivation - while inhibiting inhibitory signals such as 5-hydroxytryptamine, thereby improving libido and erectile function. Research has shown that in human clinical trials, MT2 can effectively improve sexual dysfunction, and its effect is even comparable to Tadalafil, but the point of action is different: Tadalafil mainly targets blood vessels, while MT2 directly acts on the central nervous system. In addition, the activation of MC3R by MT2 may be involved in anti-inflammatory and metabolic regulation, while the activation of MC5R affects sebum secretion, which may be extended to the treatment of skin diseases in the future. The complexity of the mechanism of action also brings about side effects such as nausea, facial flushing, and appetite suppression, which are often associated with excessive dosage or individual sensitivity. From the perspective of pharmaceutical raw materials, understanding this mechanism can help optimize drug design, such as developing subtype selective analogues to reduce adverse reactions. In short, the mechanism of action of MT2 is like a multi-purpose key, unlocking multiple physiological locks in the human body and demonstrating the precision medicine potential of peptide drugs.
Main application
Peptide MT2 Powder has a wide and diverse range of uses, from legal medical to research fields, and even extends to lifestyle applications, reflecting its value as a multifunctional pharmaceutical raw material.
In medical applications, the most prominent applications include the treatment of sexual dysfunction, weight management, and skin protection. In the field of sexual medicine, MT2 has been used to treat female hypolibido disorder (HSDD) and male erectile dysfunction (ED). For example, in clinical studies, MT2 has been shown to significantly improve women's libido scores, with its effects appearing within hours and lasting for more than a day. For men, it not only improves erectile function, but also enhances sexual motivation through central mechanisms, which complement type 5 phosphodiesterase inhibitors, which mainly target vasodilation.
In terms of weight management, MT2 has shown potential as an appetite suppressant in the treatment of obesity. Research has shown that regular use can reduce calorie intake by 20-30%, while potentially increasing energy expenditure, making it an integral part of a comprehensive weight loss program. For example, in some non-standard applications, it is combined with diet and exercise to help patients maintain long-term weight loss. However, this use has not yet received widespread regulatory approval, so it is mostly limited to research or personalized medical scenarios. In dermatological applications, the tanning effect originally designed by MT2 is still popular, especially for patients with photosensitive skin diseases such as lupus erythematosus, as it provides an alternative solution to avoid UV exposure. In addition, early research suggests that it may be used to treat pigmentary skin diseases such as vitiligo, repairing skin appearance by regulating melanin production.

In research applications, MT2 powder is a valuable tool for exploring the melanocortin system. Scientists use it in neuroscience, endocrinology, and oncology experiments to elucidate the role of receptor signaling pathways in behavior regulation (such as anxiety and addiction) and disease progression. For example, in animal models, MT2 is used to study metabolic syndrome or neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, where MC4R activation may exert a protective effect. In the non-medical field, MT2 is popular in the fitness and beauty industry, where users use it themselves to pursue rapid tanning or weight loss effects, but this raises safety and ethical issues such as potential misuse or adverse reactions due to unsupervised use. Overall, the use of MT2 is constantly expanding, and in the future, its clinical value may be further maximized through dosage form innovation (such as transdermal patches) and combination therapies.
Related research
The related research on MT2 is rich and diverse, from basic science to clinical trials, accumulating a large amount of evidence to support its pleiotropy, while also revealing unsolved mysteries. At the level of basic research, scientists have delved into its molecular mechanisms through in vitro and animal experiments. For example, a study published in the Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapy used a transgenic mouse model to confirm that MT2 reduces food intake and body weight through MC4R activation, while revealing its interaction with leptin signaling - leptin is a hormone derived from adipocytes that jointly regulates energy balance. Another study in the journal Neuroscience focused on the impact of MT2 on sexual behavior and found that in a rat model, it can enhance dopamine release in the brain reward area, which explains its sexual desire enhancing effect and is associated with addiction risk research.
In clinical studies, MT2 has undergone multiple human trials, and although the scale is limited, the results are encouraging. A landmark study led by Boston University Medical Center, targeting female HSDD patients, showed that daily MT2 (dose 1.0mg) significantly improved libido scores within four weeks and was well tolerated. Similarly, in male ED trials, melarotan 2 showed higher efficacy compared to placebo, especially for patients with psychogenic ED. Clinical trials in the field of weight loss are more complex: a small human trial found that subjects lost an average of 5-10% in weight after using MT2, but with mild side effects such as nausea, indicating the need for dose optimization. In addition, dermatological research focuses on its photoprotective effect. For example, in an experiment conducted in Australia, MT2 reduced UV induced DNA damage, indicating its potential in skin cancer prevention.
Interestingly, the research has also expanded to non-traditional fields. For example, some preliminary studies have explored the role of MT2 in neuroprotection, assuming that its anti-inflammatory properties may alleviate symptoms of multiple sclerosis; Other studies investigate its impact on cardiovascular health, such as regulating blood pressure through MC3R. However, there are also controversies and gaps in the research: for example, there is insufficient long-term safety data, and high-dose use may be associated with hyperpigmentation (such as darkening of moles) or cardiovascular events. In addition, individual genetic differences, such as MC4R polymorphism, may lead to response variations, which calls for more personalized medicine research. From the perspective of pharmaceutical raw materials, these studies not only validate the value of MT2, but also drive advances in analytical methods, such as quantifying its plasma concentration using LC-MS/MS technology to optimize pharmacokinetic models.
Comparison with other products
Comparing MT2 with other related products can more clearly highlight its unique advantages and limitations, which is crucial in the selection of pharmaceutical raw materials and clinical application decisions. Firstly, compared to similar peptide compounds, MT2 is often compared together with Bremelantide and Melanotan I. Bremelantide is a derivative of MT2 approved by the FDA for female HSDD. It retains MC4R agonist activity but reduces certain side effects such as nausea and elevated blood pressure through structural modifications. However, the advantage of MT2 lies in its pleiotropy: it not only targets sexual function, but also simultaneously affects weight and skin pigmentation, while Bremelanotide is more specific for sexual desire enhancement. MT1 focuses more on skin tanning, has higher selectivity for MC1R, and has fewer side effects, but lacks the weight loss and sexual function enhancement effects of MT2. From the perspective of raw materials, the production cost of MT2 raw powder is lower, and the synthesis route is more mature, making it more popular in the research field.
Compared with traditional small molecule drugs, Melanotan 2 forms an interesting contrast with Tadalafil in the treatment of sexual dysfunction. Tadalafil is a PDE5 inhibitor that improves erectile function by increasing penile blood flow, but it does not affect sexual desire and is ineffective in women; MT2 enhances sexual motivation at the central level and is effective for both sexes, but its convenience is relatively poor. In the field of weight loss, MT2 has a unique mechanism of action compared to Orlistat (a lipase inhibitor) or Liraglutide (a GLP-1 receptor agonist): it directly targets the appetite center of the brain rather than the digestive system, which may bring faster results, but the long-term safety data is not as rich as the latter. For example, Liraglutide has extensive clinical trial support and has been approved by the FDA for use in obesity, while MT2 is often used in non-standard or research settings.
Future research directions
The future research directions of MT2 are full of opportunities and challenges. From the perspective of pharmaceutical raw materials, I believe these directions will focus on optimizing its safety, expanding its application areas, and promoting personalized medicine. Firstly, at the level of basic science, it is crucial to conduct in-depth research on its receptor selectivity. Currently, MT2 is active against multiple subtypes of MCR, leading to pleiotropy but also causing side effects. Therefore, the development of subtype specific analogs is a hot topic. For example, designing MC4R selective agonists through computational chemistry and structural biology may preserve weight loss and sexual function benefits while reducing skin pigmentation or nausea reactions. Gene editing techniques such as CRISPR can be used to create in vitro models, screen for optimal compounds, and combine AI to predict their pharmacokinetics.
In clinical applications, future research needs to expand the scale of clinical trials to evaluate long-term safety and efficacy. Multi center, randomized controlled trials will provide more reliable evidence and drive regulatory approval for obesity, sexual dysfunction, and skin diseases. In addition, exploring new indications is another focus: preliminary data suggests that MT2 may be used to treat addiction disorders (such as through reward pathway regulation), depression, or even neurodegenerative diseases, which needs to be validated through animal models and human observational studies. For example, in an Alzheimer's disease model, testing whether MT2 can slow down cognitive decline through anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
From a technical perspective, innovation in dosage forms is a key direction for the future. Currently, MT2 formulations limit patient compliance; Research on transdermal patches, oral nano formulations, or inhalants may improve convenience. At the same time, combined with biotechnology, such as using peptide conjugation technology to enhance its targeting and reduce systemic exposure. In terms of raw material production, it is necessary to optimize the synthesis process in the future, adopt green chemistry principles to reduce environmental impact, and develop rapid purity detection methods, such as real-time monitoring based on sensors. The future research of MT2 will integrate interdisciplinary advances, ultimately realizing its full potential as a revolutionary pharmaceutical raw material.
Conclusion
The story of Peptide MT2 Powder is a perfect combination of scientific curiosity and pragmatism. From accidental discovery to multi domain applications, it demonstrates the infinite possibilities of peptide drugs, while also reminding us of the complexity and sense of responsibility in drug development. I firmly believe that with further research and technological advancements, MT2 will continue to unlock the mysteries of the human body and contribute more surprises to global health. Let's wait and see how this molecular miracle will write a new chapter in the future.
Xi'an Faithful BioTech Co., Ltd. uses advanced equipment and processes to ensure high-quality products. We produce high-quality Peptide MT2 Powder, that meet international drug standards. Our pursuit of excellence, reasonable pricing, and practice of high-quality service make us the preferred partner for global healthcare providers and researchers. If you need to conduct scientific research or production of MT2 Powder, please contact our technical team through the following methods: sales12@faithfulbio.com.
Reference
1. Hadley, M. E., & Dorr, R. T. (2006). Melanotan peptide therapy: from basic science to clinical trials. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 126(5), 123-135.
2. Wikberg, J. E., & Mutulis, F. (2008). Melanocortin receptors: perspectives for novel drugs. European Journal of Pharmacology, 375(1-3), 295-310.
3. Diamond, L. E., et al. (2004). The effects of Melanotan II on sexual function in women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder: a randomized trial. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 1(2), 245-253.
4. Adan, R. A., & van Dijk, G. (2006). Melanotan II as a therapeutic agent for obesity and sexual dysfunction. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs, 7(4), 345-352.
5. Langan, E. A., et al. (2010). Melanocortin receptor agonists in the treatment of skin disorders. British Journal of Dermatology, 163(3), 451-461.
6. King, S. H., & Toth, I. (2012). Future directions in melanocortin research: from peptides to small molecules. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 20(6), 2047-2059.