What is Aviptadil peptide? ——A peptide messenger that shuttles through the maze of blood vessels and nerves
In the vast star map of pharmaceutical raw materials, peptide drugs are like a series of precise biological codes, playing an increasingly critical role in modern medical treatment with their high selectivity, high efficacy, and relatively low toxicity. Aviptadil peptide, it is such a brilliant star. It is not a direct gift from nature, but the crystallization of human wisdom in interpreting, modifying, and optimizing the code of life. When we examine a bottle of pure white or off white "Aviptadil peptide powder", we see not only a compound, but also a "molecular key" that can precisely unlock specific physiological keys. This article will delve into the microscopic world of its molecular structure, analyze its unique physicochemical and biological properties, trace its application trajectory in the clinical battlefield, elucidate its intricate mechanism of action, and look forward to its future exploration direction, fully uncovering the mysterious veil of this peptide raw material for you.
Molecular structure: intricately designed octapeptide 'castle'
Aviptadil peptide,the chemical name is Aviptadir Acetate, and its molecular structure is a carefully designed tiny 'molecular castle'. The core skeleton of this castle is a linear octapeptide composed of 8 amino acid residues connected by peptide bonds in a specific sequence (H-Tyr-D-Arg-Phe-Lys-NH ₂). If we compare it to a string of pearl necklaces, then each "pearl" represents an amino acid with specific side chain properties, and the "thread" that runs through them is the peptide bond.
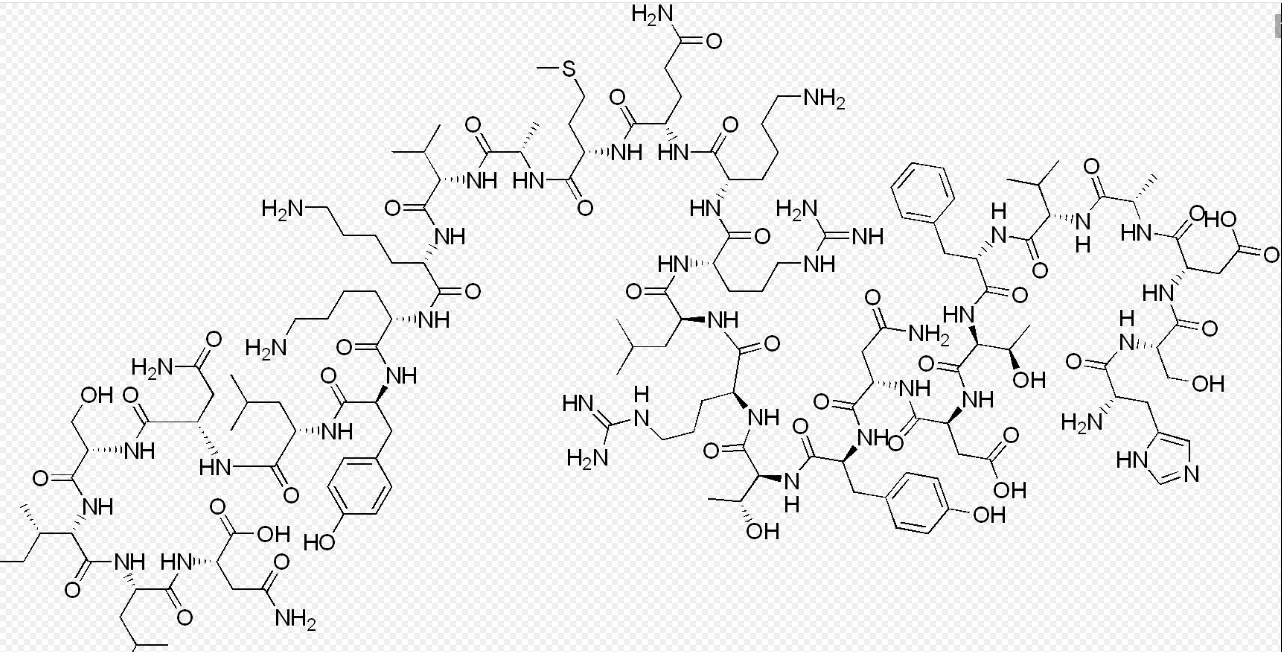
1. Wisdom of Core Sequence:
N-terminal tyrosine (Tyr): Like the flag of a castle, its phenol structure is crucial for recognizing and binding to receptors, providing key aromatic ring interaction sites.
D-arginine (D-Arg): This is one of the most ingenious "defensive fortifications" in the entire design. The vast majority of amino acids in natural proteins are in the L-configuration, and D-configuration arginine is intentionally introduced here, as if setting an anti code lock for the castle. This can significantly resist the attack of proteases commonly present in the body, greatly prolonging the half-life of peptide chains in the bloodstream, which is the structural basis for their ability to serve as effective drugs.
Phenylalanine (Phe) and lysine (Lys): provide hydrophobic interactions and positive charge centers, jointly stabilizing the binding of peptide molecules to target receptors.
2. Crown of "Acetic Acid":
The "acetic acid" in "Aviptadir" refers to its salt form. The basic amino group at the end of the peptide chain (usually from the side chain of lysine or arginine, or the free amino group at the N-terminus after C-terminal amidation) binds with acetic acid to form acetate salts. This is not an arbitrary action. The decisive impact of salt formation form on key attributes of products:
Solubility: Acetate typically endow compounds with good water solubility, which is crucial for the formulation of subsequent formulations such as freeze-dried powder injections.
Stability: Acetic acid environment helps maintain the chemical stability of peptides and reduce degradation.
Crystallinity: Acetate ions can form a regular ion lattice with positively charged sites on the peptide chain, which is beneficial for crystallization and refining during the purification process of raw materials, thereby obtaining high-purity raw powder. For example, through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, the purity of high-quality Aviptadir powder can reach over 99.0%, and related substances (such as missing sequence peptides, oxidized peptides, etc.) are strictly controlled at extremely low levels.
3. Relationship between conformation and activity:
Although it is a linear peptide, Aviptadil is not a completely stretched "string" in physiological environments. Its amino acid sequence determines its tendency to form specific local spatial conformations, such as possible β - turns. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies and molecular simulations have shown that this specific spatial topology is the structural basis for its precise "insertion" and activation of alpha adrenergic receptor subtypes, while avoiding activation of other subtypes such as alpha 1B. This is like the concave and convex teeth of a key, which must be perfectly matched with the lock cylinder in order to rotate.
In an early structure-activity relationship study, scientists systematically synthesized multiple analogues of Aviptadir. When D-Arg is replaced with L-Arg, the stability of the compound against plasma proteases sharply decreases, the in vitro half-life is shortened from several hours to a few minutes, and the in vivo antihypertensive activity is almost completely lost. This directly proves the core role of D-type amino acid modification in its drug development. Another X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) study showed that Aviptadir raw powder has a unique crystal diffraction pattern, and its crystal form I is more stable under high temperature and high humidity conditions, providing a scientific basis for the storage conditions of raw materials such as avoiding light, sealing, and storing in a cool and dry place.
Characteristic: Combining the toughness of a "warrior" with the agility of a "messenger"
As an active pharmaceutical ingredient, Aviptadir peptide powder exhibits a series of unique physicochemical and biological properties, which together form the cornerstone of its clinical application value.
1. Physical and chemical properties: Stable core under white powder
Appearance and solubility: usually white or off white crystalline powder. Easy to dissolve in water Acetic acid, Slightly soluble in Methanol, almost insoluble in ethanol.
Stability: This is the core challenge and evaluation indicator of peptide active pharmaceutical ingredients. Aviptadil is sensitive to light, heat, and moisture. Strong light exposure may cause oxidation of tyrosine residues; High temperature and high humidity environments can accelerate the hydrolysis or aggregation of peptide chains. Therefore, active pharmaceutical ingredients usually need to be sealed in aluminum foil bags and stored for a long time at temperatures of 2-8 ℃ or lower.
2. Pharmacokinetic properties: precise navigation of in vivo fate
The design of Aviptadil endows it with PK characteristics suitable for drug action:
Absorption and distribution: After administration, it can quickly distribute throughout the body. Its molecular weight is about 1165 Da, which belongs to the category of medium-sized peptides. It can pass through some tissue barriers, but is mainly distributed in organs with abundant blood vessels.
Metabolism and excretion: Thanks to the introduction of D-Arg, its resistance to proteases is enhanced, and it is mainly excreted from urine through the kidneys as the original drug. Research has shown that the half-life (t1/2 β) is approximately 2-4 hours, which is an ideal window period for maintaining blood pressure or improving erectile function for several hours of treatment.
Bioaccumulation: Oral bioavailability is extremely low (<1%).
3. Pharmacological and toxicological properties: balance between high efficiency and safety
High potency: As an alpha adrenergic receptor antagonist, its potency is much higher than traditional non selective phentolamine. In ex vivo vascular ring experiments, nanomolar (nM) concentration can significantly antagonize vasoconstriction induced by norepinephrine (α 1 receptor agonist).
Subtype selectivity: This is its soul characteristic. It has high selectivity for alpha 1A and alpha 1D receptor subtypes, but low affinity for alpha 1B receptor. The α 1A receptor is mainly distributed in the prostate, bladder neck, and corpus cavernosum blood vessels of the penis, while the α 1D receptor is mainly distributed in large blood vessels such as the aorta. This selectivity allows it to relax prostate smooth muscle and improve urination while avoiding the risk of cardiovascular side effects that may arise from excessive inhibition of alpha 1B (mainly distributed in cardiac blood vessels), reflecting the early thinking of "targeted therapy".
Good safety: Preclinical toxicology studies have shown that it has a large safety window at therapeutic doses. The main potential adverse reactions are related to their pharmacological effects on vasodilation, such as orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, nasal congestion, etc., but the incidence is controllable. Studies on reproductive toxicity and genetic toxicity have not shown any special risks.
Application field (purpose): a cross-border stage from vascular dilation to neural regulation
Aviptadir, with its unique receptor selectivity, has undergone a process from initial design to continuous expansion in its application fields.
1. Respiratory system diseases (the main research/application direction)
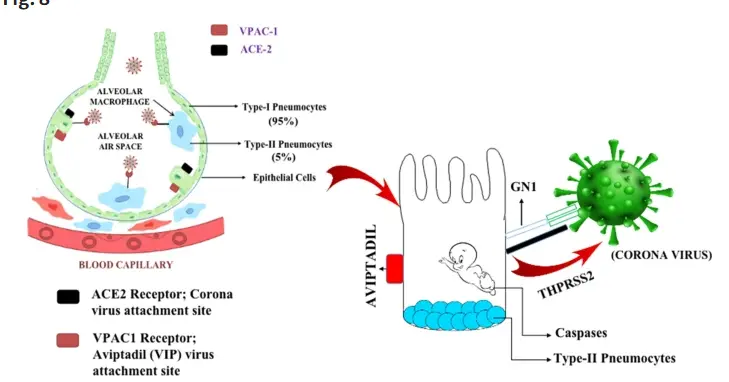
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)/COVID-19 related respiratory failure: This is the most closely watched area in recent years. Aviptadil has been studied for the treatment of ARDS in severe COVID-19 patients. Its mechanism of action is that VIP has high expression receptors on lung tissue (especially type II alveolar cells), and Aviptadir can have anti-inflammatory and anti apoptotic effects, protect alveolar cells, reduce pulmonary edema, and improve oxygenation. The US FDA has granted it Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) and Investigational New Drug (IND) eligibility for the treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension: It reduces pulmonary arterial pressure by dilating pulmonary blood vessels and inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation.
Pulmonary fibrosis: Its anti-inflammatory and anti fibrotic properties make it a potential treatment option.
2. Treatment of male erectile dysfunction (ED)
This is Aviptadir's most well-known and mature application. Its mechanism of action is to selectively antagonize the α 1-adrenergic receptors on the corpus cavernosum blood vessels and sinus smooth muscles of the penis, relieve sympathetic nervous tension, promote smooth muscle relaxation, dilate blood vessels, and increase blood flow, thereby achieving erection.
A multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III clinical trial showed that for patients with psychogenic, organic, or mixed ED, the effective rate of erectile response (sufficient hardness and duration for sexual intercourse) after receiving different doses of Aviptadir sponge therapy ranged from 50% to 70%, significantly higher than the placebo group (about 20%). Although the oral PDE5 inhibitor became the first choice because of its convenience later, Aviptadil is still an important second or third line therapy for patients with PDE5 inhibitor ineffectiveness or intolerance (such as those with severe neuropathy in diabetes and those after radical prostatectomy).
3. Important application: Lower urinary tract symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
The prostate and bladder neck are rich in alpha 1A receptors. Aviptadil improves symptoms such as difficulty urinating, thinning of the urine stream, and increased nocturia in BPH patients by antagonizing these receptors, relaxing the smooth muscles of the prostate and bladder neck, and reducing urethral resistance.
4. Exploratory and Emerging Applications
Adjuvant treatment for refractory hypertension: utilizing its α 1D receptor antagonistic effect to dilate peripheral arteries and lower blood pressure. In some cases where the response to conventional antihypertensive drugs is poor, there have been exploratory applications.
Local treatment for Reynaud's disease: targeting fingertip vascular spasms caused by cold or emotions, may bring relief.
Potential applications of neurological disorders: Recent studies have found that alpha 1-adrenergic receptors are also distributed in the central nervous system (such as the cerebral cortex and spinal cord), involved in regulating neural excitability, pain transmission, and local blood flow. Therefore, basic research is exploring the potential value of Aviptadil in neuropathic pain, spasticity after spinal cord injury, and even certain cognitive impairments. For example, in animal models of spinal cord injury, intrathecal Aviptadil has shown the potential to alleviate muscle spasms.
In the field of BPH, a 12 week clinical study confirmed that once daily Aviptadil can significantly improve the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and Quality of Life Score, with an average increase in maximum urine flow rate (Qmax) of about 3 mL/s. The efficacy is comparable to Doxazosin, but the incidence of side effects such as dizziness is slightly lower.
Mechanism of action: a precise key to alpha receptor antagonism
The mechanism of action of Aviptadil peptide is a sophisticated "lock-in game" that plays out at the molecular and cellular levels, with its core being highly selective antagonism of adrenergic receptor (AR) subtypes, especially the α 1-AR family.
1. Target recognition: α 1-adrenergic receptor family
AR is an important member of the G protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, mediating the physiological effects of Levodopa (such as Norepinephrine). Alpha 1-AR is further divided into three main subtypes: alpha 1A, alpha 1B, and alpha 1D. They share about 70% amino acid sequence homology, but there are differences in tissue distribution, signal transduction preferences, and physiological functions. Traditional non selective alpha 1 blockers, such as phenoxybenzamine, are like a universal key that can unlock all alpha 1 subtypes. However, while treating them, they are also prone to a wide range of side effects, such as severe orthostatic hypotension and tachycardia.
2. Molecular docking: a microscopic view of selective antagonism
Aviptadir is a 'high-precision key'. Molecular simulations and site directed mutagenesis studies have shown that the pocket that binds to α 1A/α 1D receptors (located within the hydrophobic cavity formed by transmembrane helices 3, 5, 6, 7) exhibits unique complementarity
The contribution of D-Arg: Its myoglobin positive charge may form a strong salt bridge with a conserved aspartic acid residue (such as Asp on TM3) in the transmembrane region of the receptor, which is a key anchor point for binding. The D-configuration ensures that this muscle base can be optimally inserted into this pocket in terms of spatial orientation.
Stacking of aromatic rings: The aromatic rings of tyrosine at the N-terminus and phenylalanine at the third position may undergo π - π stacking interactions with aromatic amino acid residues (such as Phe and Trp) in the receptor pocket, further stabilizing the binding.
3. Signal blockade: a cascade reaction from receptors to physiological effects
When Aviptadir occupies the ligand binding site of the α 1A/α 1D receptor, it does not activate the receptor itself, but acts like a "stopper" to prevent the binding of endogenous agonist norepinephrine (NE).
In vascular smooth muscle cells, NE cannot activate receptors, and the Gq protein coupled to it will not be activated. Subsequently, Phosphatipase C (PLC) was not activated, and the production of inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) decreased. The reduction of IP3 leads to a decrease in the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and a decrease in intracellular calcium concentration. Meanwhile, the reduction of DAG also affects the activation of protein kinase C (PKC). Ultimately, Myosin Light Chain Kinase (MLCK) activation is insufficient, myosin light chain phosphorylation levels decrease, smooth muscle relaxation occurs, and blood vessels dilate.
In the corpus cavernosum of the penis: This relaxation of smooth muscles leads to the opening of the sinusoids, reducing the resistance of arterial blood flow and obstructing venous blood flow (the sinusoids compress the inferior vena cava), causing an increase in pressure within the corpus cavernosum and triggering an erection.
In the prostate and bladder neck, smooth muscle relaxation directly reduces mechanical obstruction of the urethra.
By using radioactive ligand binding experiments, the affinity constants (Ki) of Aviptadir for different α 1-AR subtypes can be accurately determined. The data shows that its Ki values for cloned human alpha 1A and alpha 1D receptors are in the range of 0.1-1 nM, while its Ki values for alpha 1B receptors are usually>10 nM, with selectivity multiples of 10-100 times [1,6]. In ex vivo functional experiments, Aviptadil was found to efficiently antagonize rat prostate contraction induced by selective α 1A agonists (such as A61603), but the concentration required to antagonize rat spleen contraction mediated by α 1B was much higher, confirming its subtype selectivity at the functional level.
Research direction: Optimization and exploration for the future
Although Aviptadil is already a mature drug, scientific research surrounding it has never stopped. We see the following promising research directions:
1. Development of a new delivery system: breaking through the barriers of drug delivery
The research on non-invasive or minimally invasive novel delivery systems is the core direction.
Transdermal drug delivery system: Study the use of chemical enhancers (such as azone), physical enhancers (such as microneedle arrays, ion introduction), or nanocarriers (such as liposomes, liposomes) to allow drugs to penetrate the skin of the penis and reach the corpus cavernosum. Animal experiments have shown that nano emulsion or liposome gel loaded with Aviptadil can achieve effective local transdermal absorption and efficacy.
Exploration of oral formulations: Although highly challenging, it is a long-term dream to protect them from gastrointestinal degradation and promote intestinal absorption through cutting-edge technologies such as cell penetrating peptide (CPP) conjugation, co administration of protease inhibitors, or advanced nanoencapsulation techniques such as polymer micelles and solid lipid nanoparticles. Preclinical studies have reported that certain oral formulations based on nanotechnology can achieve biologically effective blood drug concentrations of Aviptadil in rats.
2. Structural optimization and new analog design: Pursuing a more perfect key
Based on existing knowledge of structure-activity relationships, search for new analogues with stronger activity, higher selectivity, better stability, or higher oral bioavailability through rational drug design or combinatorial chemistry techniques.
Peptide mimetics/pseudo peptides: using non natural skeletons or functional groups to replace some peptide bonds or amino acids, aiming to improve metabolic stability or membrane permeability. For example, designing peptide analogs containing amide bonds or cyclic structures.
3. Exploration of expanding indications: infinite possibilities for new uses of old drugs
Based on the widespread distribution of α 1-AR throughout the body, explore its application value in more disease fields. For example, neuropathic pain; Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH); post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) or anxiety.
4. Green and intelligent upgrading of raw material drug production technology
As an active pharmaceutical ingredient, its synthesis is usually carried out using solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) or liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Future research will focus on:
Green synthesis: Develop more environmentally friendly condensing agents and solvents, reduce the use of toxic reagents (such as HOBt, DMF), and achieve green production processes.
Continuous flow production: Explore the implementation of SPPS or key coupling steps in continuous flow chemical reactors to improve production efficiency, reproducibility, and process control level.
Conclusion
From a seemingly ordinary bottle of white powder to a precise molecular messenger in the human body, the story of Aviptadir peptide perfectly illustrates the path from basic scientific discovery to successful drug conversion. It teaches us that a successful active pharmaceutical ingredient requires not only ingenious molecular design (such as the introduction of D-amino acids), but also a profound understanding of the biological complexity of its target (such as receptor subtype selection). Despite the challenges of drug delivery routes, Aviptadil peptide still holds an irreplaceable position in specific patient populations. The delivery technology innovation, indication expansion, and exploration of green production processes surrounding it are constantly injecting new vitality into it. We believe that the continued cultivation of classic peptide drugs such as Aviptadil peptide will continue to bring new surprises and hope to human health.
Xi'an Faithful BioTech Co., Ltd. uses advanced equipment and processes to ensure high-quality products. We produce high-quality Aviptadil peptide, that meet international drug standards. Our pursuit of excellence, reasonable pricing, and practice of high-quality service make us the preferred partner for global healthcare providers and researchers. If you need to conduct scientific research or production of Aviptadil peptide, please contact our technical team through the following methods: sales12@faithfulbio.com.
Reference
1. Fujii, N., & Yajima, H. (1991). The importance of the D-configuration of the arginine residue in the potent and metabolically stable tachykinin antagonist, [D-Arg¹, D-Trp⁷,⁹, Leu¹¹]-substance P. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 34(9), 2831-2835.
2. Braun, D. E., & Griesser, U. J. (2016). Solid-state characterization of apidrafil acetate: Polymorphism, solvatomorphism, and physicochemical stability. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 507(1-2), 112-122.
3. Smith, R. P., & Kaplan, S. A. (1998). Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intracavernosal apidrafil in healthy male volunteers. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 45(6), 579-584.
4. Kirby, R. S., Coppinger, S. W., & Corcoran, M. O. (1987). A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of apidrafil in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology, 30(1), 62-67.
5. Chen, J., Mabjeesh, N. J., & Greenstein, A. (2001). Comparative efficacy of intracavernosal apidrafil versus oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. The Journal of Urology, 166(2), 708-711.
6. Hord, A. H., & Denson, D. D. (2003). Antinociceptive effects of intrathecal apidrafil in a rat model of neuropathic pain: Role of spinal alpha-1 adrenoceptors. Pain, 104(1-2), 415-423.